11 The Arts
Creativity and Development
Tanessa Sanchez and Kerry Diaz
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you should be able to:
An Introduction to Arts Education
Arts education plays a crucial role in fostering physical, cognitive, and emotional development in children. When children engage in activities like drawing, dancing, or playing musical instruments, they develop fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination. For example, activities like painting or sculpting require children to use small muscles in their hands, which helps them build physical dexterity and precision. Similarly, learning to play an instrument or participating in dance involves movement and body control, which enhances gross motor skills and spatial awareness. These physical skills are foundational for overall development and contribute to a child’s ability to engage in a variety of daily tasks, from writing to playing sports.
Cognitively, arts education provides children with opportunities to enhance problem-solving skills and critical thinking. For instance, when children compose a piece of music, solve a complex drawing, or perform a play, they learn to make decisions, think creatively, and consider different perspectives. Art encourages children to experiment, take risks, and learn from their mistakes, fostering a growth mindset. Studies have shown that children who participate in the arts tend to perform better academically because they are more adept at thinking critically, organizing ideas, and developing strong memory skills. Furthermore, the arts support language development as children often expand their vocabulary and narrative abilities through storytelling, acting, or analyzing lyrics.
Emotionally, the arts provide a powerful outlet for self-expression, helping children process and understand their feelings. Engaging in creative activities allows children to express emotions they may not be able to articulate verbally. Whether through painting, writing, or performing, children can explore their identities and gain confidence in their ability to express themselves. The arts also provide a sense of accomplishment and pride, boosting self-esteem. Additionally, participating in group art activities, such as theater or music ensembles, promotes social-emotional skills, such as teamwork, empathy, and communication. Overall, arts education helps children develop emotionally by nurturing their ability to handle emotions, relate to others, and navigate the complexities of their inner worlds.
Visual Arts
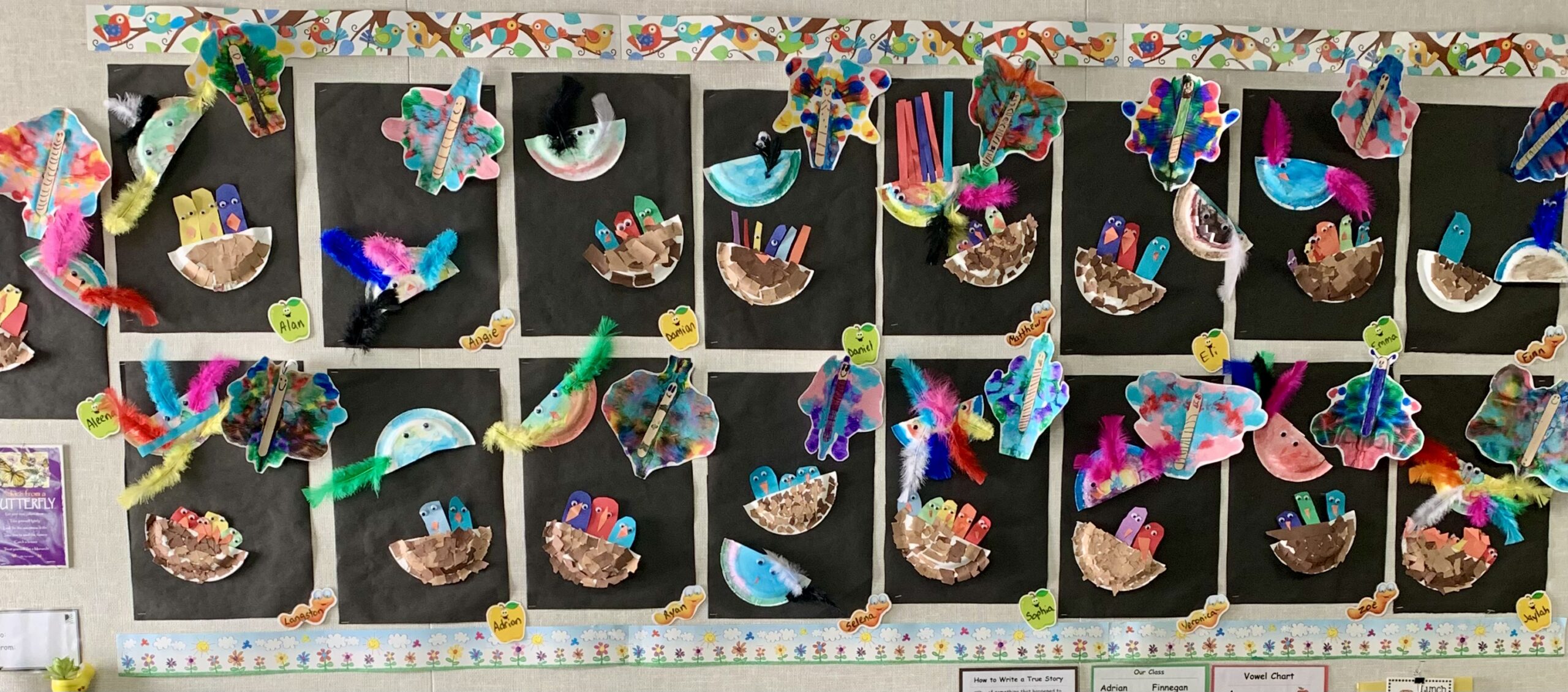

In elementary and middle school, visual arts education plays a vital role in fostering creativity, self-expression, and critical thinking while also supporting the development of fine motor skills and spatial awareness. In these early years, students are encouraged to explore a wide range of art materials and techniques, allowing them to express their ideas and emotions in unique ways. The focus is often on experimentation, personal expression, and the exploration of different artistic mediums, while also introducing basic principles such as color theory, composition, and perspective. By engaging in visual arts, students also develop their ability to observe, analyze, and respond to the world around them, which enhances their cognitive and emotional development.
For middle school students, the focus shifts slightly toward refining technical skills while still emphasizing creativity and self-expression. Students begin to explore more advanced techniques, such as shading, blending, and more complex compositions, while being encouraged to incorporate their personal interests and experiences into their artwork. At this level, art education becomes more interdisciplinary, connecting visual arts with history, culture, and other subject areas, which helps students see the broader significance of art. It also provides opportunities for students to collaborate, critique their work, and reflect on the creative process, contributing to the development of social and emotional skills.
Visual Art Activities for Elementary and Middle School Programs
- Drawing from Observation: Students practice sketching objects, people, or scenes they observe directly, helping improve fine motor skills and attention to detail.
- Collage Making: Using magazines, newspapers, and other materials, students create artwork by assembling pieces into new compositions, fostering creativity and texture exploration.
- Painting with Watercolors or Acrylics: Students experiment with different painting techniques, such as layering colors and blending, while learning about color theory.
- Sculpture with Clay: Working with modeling clay, students create three-dimensional art, improving hand-eye coordination and spatial awareness.
- Printmaking: Students explore printmaking techniques such as linocut or monoprint, learning about texture and repetition in art.
- Mixed Media Projects: Combining various materials (e.g., paint, fabric, paper, or found objects), students create multi-layered works of art, encouraging innovation and resourcefulness.
- Abstract Art Exploration: Students are encouraged to express their emotions or ideas through abstract forms and colors, developing self-expression and critical thinking.
- Paper Mâché Creations: Students create sculptures or masks by layering paper and glue, learning patience, and practicing construction techniques.
- Photography Projects: Using digital or film cameras, students capture images that tell a story, develop an eye for composition, and explore the role of light and shadows.
- Art Exhibitions: Students prepare and showcase their artwork for an exhibition, learning how to present their work and reflect on their creative process.
These activities not only help develop artistic skills but also foster confidence, problem-solving abilities, and an appreciation for diverse forms of expression. Through visual arts, students in elementary and middle school can explore their creativity and develop skills that benefit them academically, emotionally, and socially.
Music
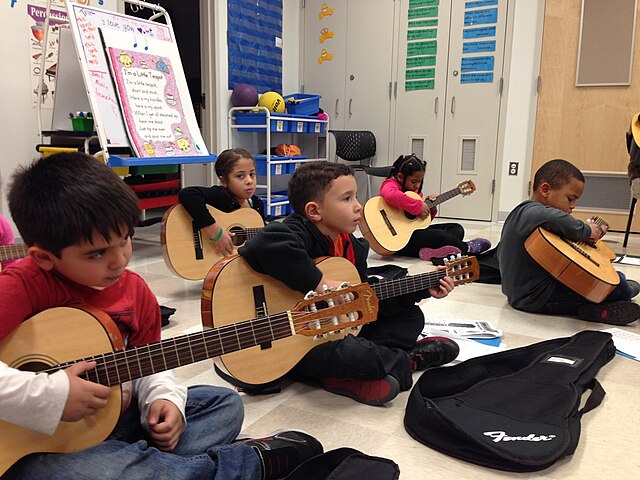

Music education in elementary and middle schools plays a significant role in children’s cognitive, emotional, and social development. It fosters creativity, enhances listening skills, and improves academic performance by reinforcing concepts from other subjects, such as math, language, and history. In elementary school, the focus is on building a foundation of musical skills, introducing basic concepts such as rhythm, melody, and harmony, while encouraging students to explore different instruments and vocal techniques. Activities are often designed to help children develop ear training, singing skills, and an appreciation for music from various genres and cultures.
In middle school, music education becomes more advanced, offering opportunities for students to deepen their understanding of music theory, refine their instrumental skills, and explore different types of music more seriously. Students may have the chance to participate in school bands, choirs, or orchestras, and music education becomes a platform for collaboration, as students learn to play in ensembles, create original compositions, and perform in front of an audience. It is also a time when music can be used to explore historical contexts, cultural differences, and the evolution of musical genres, allowing students to gain a broader understanding of music’s role in society.
Music Activities For Elementary and Middle School Programs
- Rhythm Clapping Exercises: Students clap different rhythms to develop an understanding of beats, tempo, and time signatures.
- Singing Simple Songs: Children practice vocal techniques while singing age-appropriate songs, developing pitch, tone, and harmony.
- Instrument Exploration: Students try out a variety of percussion instruments (drums, tambourines, maracas) to understand rhythm and sound production.
- Call and Response Songs: Teachers lead students in call-and-response singing, helping them develop listening skills and vocal synchronization.
- Creating Soundscapes: Students work in groups to create soundscapes using instruments or their voices, exploring the ways music can evoke emotion or represent scenes and environments.
- Group Ensemble Performances: Students collaborate in small groups to play simple compositions together, learning to follow musical cues and work as a team.
- Music Composition: Students write their own simple melodies or rhythms, encouraging creativity and an understanding of musical structure.
- Learning Basic Music Notation: Students practice reading and writing basic music notes, rhythms, and time signatures to develop music literacy.
- Listening to Diverse Music Genres: Students listen to and discuss music from different cultures and historical periods, expanding their appreciation for various musical styles.
- School Performances and Concerts: Students participate in school concerts or talent shows, showcasing their vocal or instrumental skills and building confidence in performance.
Music education in elementary and middle schools not only enhances students’ musical abilities but also helps develop skills like discipline, concentration, and emotional expression. It provides a creative outlet for children and supports their ability to collaborate, listen, and communicate effectively. Through these activities, students gain a lifelong appreciation for music while improving cognitive and social skills that extend well beyond the music classroom.
Drama

Drama education in elementary and middle schools plays a vital role in the social, emotional, and cognitive development of students. It encourages self-expression, enhances communication skills, and builds confidence as students participate in activities that involve role-playing, storytelling, and performing. In elementary school, drama is often integrated into lessons that combine creative play with learning, focusing on the basics of improvisation, characterization, and movement. Drama education allows children to explore emotions, practice collaboration, and gain a better understanding of perspective-taking by stepping into the shoes of different characters.
In middle school, drama education becomes more structured, offering students opportunities to deepen their understanding of performance techniques, including stage presence, voice projection, and character development. Students may engage in more complex activities, such as performing scenes from plays, writing their own scripts, and collaborating in small groups to create performances. Drama education in middle school also fosters important social-emotional skills, such as teamwork, empathy, and conflict resolution, as students learn to interact and communicate effectively both on and off stage. Additionally, students begin to analyze the deeper meaning of characters, themes, and stories, which enriches their ability to think critically and express themselves thoughtfully.
Drama Activities for Elementary and Middle School Programs
The following activities are meant to foster creativity, self-expression, and social skills.
- Improvisation Games: Students engage in spontaneous role-playing games, which encourage creativity and quick thinking. Examples include “Yes, And” where participants build on each other’s ideas, and “Freeze,” where players freeze mid-action and create new scenes on the spot.
- Role-Playing: Students assume different characters and act out scenarios to practice empathy and perspective-taking. This activity allows students to step into diverse roles and explore emotions.
- Storytelling: Students take turns telling parts of a story, incorporating gestures and voices to make the narrative engaging. This promotes confidence in speaking and the development of narrative skills.
- Tableaux: Students work in groups to create frozen pictures (tableaux) that represent a scene, an emotion, or a story. This activity helps students focus on body language and teamwork.
- Character Development: Students create and perform short monologues from the perspective of a character they have developed, exploring their motivations, emotions, and personality traits.
- Mime and Pantomime: Students practice conveying emotions and actions without words, using only gestures and body movement. This strengthens their non-verbal communication skills and enhances physical awareness.
- Costume and Prop Design: Students participate in designing costumes and props for performances, learning about the visual aspects of storytelling and the role of design in bringing a character to life.
- Group Scene Work: Small groups of students rehearse and perform short scenes from plays or stories, which helps develop teamwork, collaboration, and the ability to interpret text.
- Script Writing: Students write short scripts based on their ideas or real-life situations, encouraging creativity, storytelling, and writing skills.
- Drama Circles: The class forms a circle and each student shares an emotion or thought through movement or sound, building on each other’s contributions. This activity encourages listening, creativity, and group cohesion.
Drama education in elementary and middle school provides students with tools to express themselves, develop empathy, and build strong interpersonal skills. By engaging in drama activities, children learn to communicate more effectively, resolve conflicts, and collaborate with others in meaningful ways. The skills learned through drama extend to other areas of learning, helping students become more confident, creative, and thoughtful individuals.
Dance
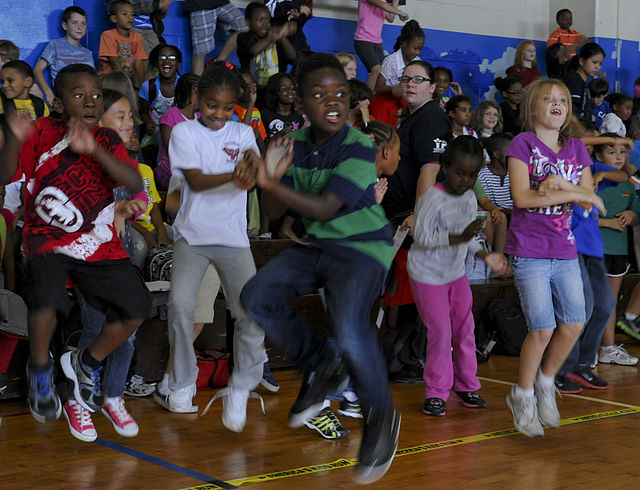
Dance education in elementary and middle schools provides students with an important avenue for creative expression, physical development, and emotional growth. In the early grades, dance is often introduced as a way for children to explore movement, develop coordination, and understand rhythm. Students engage in structured and unstructured dance activities, using their bodies to express emotions, tell stories, and connect with music. This process not only enhances motor skills, balance, and flexibility but also improves social-emotional learning by encouraging self-confidence, teamwork, and cooperation. Dance allows students to develop body awareness and understand how to control and express movement in space, which benefits both physical and cognitive development.
As students progress into middle school, dance education becomes more structured, and students begin to explore more complex styles and techniques, such as ballet, jazz, hip-hop, or contemporary dance. The focus shifts to refining movement, learning choreography, and understanding dance in a cultural and artistic context. Middle school dance education encourages students to interpret music and emotions through movement, strengthening their creativity and emotional intelligence. It also fosters collaboration as students may work together to choreograph performances, teaching them valuable teamwork and communication skills. Dance performances or recitals offer students opportunities to develop self-expression, confidence, and public speaking abilities, all while enjoying the physical and artistic benefits of movement.
Dance Activities for Elementary and Middle School Programs
- Creative Movement: Students explore different ways their bodies can move to music, experimenting with different types of motion such as stretching, twisting, and jumping, which develops body awareness and coordination.
- Dance Improvisation: Students create spontaneous movements based on a particular theme, emotion, or rhythm, allowing for creativity and self-expression while building flexibility and spontaneity in movement.
- Rhythm and Coordination Games: Students practice clapping, tapping, or stomping in sync with music or patterns, helping to develop a sense of timing and rhythmic accuracy.
- Basic Dance Technique: Students are introduced to the fundamentals of different dance styles (ballet, jazz, hip-hop), learning core positions and movements that will support further skill development.
- Partner or Group Dance: Students work together in pairs or small groups to perform basic choreography, teaching them how to collaborate, share space, and synchronize movements.
- Storytelling through Dance: Students interpret a story or theme through movement, developing their ability to express emotions and narratives without words.
- Cultural Dance Exploration: Students learn dances from various cultures, such as African, Latin, or folk dances, broadening their understanding of dance as an artistic and cultural form of expression.
- Choreography Projects: Students work individually or in groups to create their own short dance routines, exploring their creativity and understanding how to combine movements into a cohesive performance.
- Mirror Dance: One student leads a sequence of movements, and the others mirror them, which helps with focus, precision, and empathy as students mimic the leader’s movements.
- Dance Reflection and Journaling: After performing or creating choreography, students reflect on their experiences through writing or group discussions, deepening their understanding of movement and the emotions they expressed through dance.
Dance education not only benefits students physically by improving muscle strength, balance, and flexibility, but it also fosters creativity, self-expression, and social connections. In elementary and middle school, dance helps students develop important life skills, including discipline, confidence, and collaboration, while offering them a creative outlet to explore their emotions and ideas. Through dance, students gain an appreciation for movement as an artistic form and a tool for personal and social growth.
Media Arts
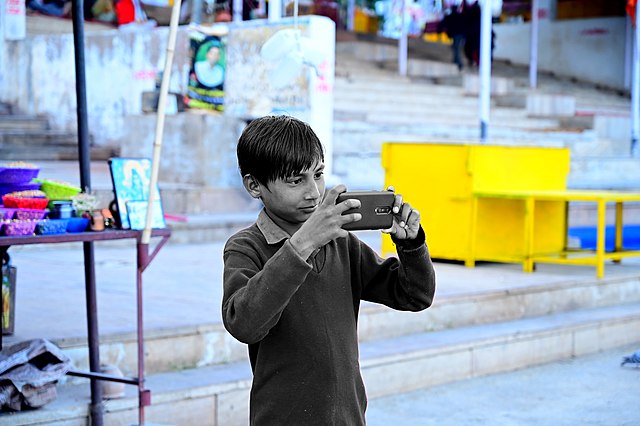

Media arts education in elementary and middle schools introduces students to the world of digital storytelling, video production, photography, graphic design, and other forms of media communication. This area of arts education helps students develop visual literacy, creativity, and technical skills while exploring the ways in which media can be used to express ideas, tell stories, and communicate messages. In elementary school, media arts often focus on developing an understanding of basic media concepts through simple projects such as photography, drawing, and basic video creation. These early experiences encourage creativity, problem-solving, and self-expression through a variety of digital tools.
As students progress to middle school, media arts education becomes more structured, introducing them to more sophisticated technology and techniques such as film editing, graphic design software, and digital animation. They begin to explore how media is created, edited, and presented across different platforms. Media arts also foster critical thinking as students analyze the impact of media on society and reflect on how messages are conveyed visually and aurally. Middle school students have more opportunities to engage in hands-on projects, where they develop technical skills and creativity, and they often work on collaborative projects that help them learn the importance of teamwork and communication.
Media Arts Activities for Elementary and Middle School Programs
- Digital Photography: Students learn the basics of taking photographs with a digital camera, focusing on elements like composition, lighting, and framing, and then use editing software to enhance their images.
- Stop Motion Animation: Students create short animations using stop-motion techniques, photographing objects or drawings frame-by-frame and then compiling them into a video.
- Storyboarding: Students learn how to plan out a story visually through the use of storyboards, mapping out scenes and camera angles before creating a short film or animation.
- Video Editing: Students shoot video footage and learn to edit their footage into a cohesive story using basic editing software, exploring transitions, sound effects, and titles.
- Creating a Podcast: Students write, record, and edit their own podcasts, developing skills in audio production and learning how to communicate ideas clearly and engagingly.
- Designing Posters or Flyers: Students use graphic design software to create promotional materials like posters or flyers for an event, developing their visual communication and layout skills.
- Creating Digital Comics: Students design and create their own digital comics, combining drawing and writing skills to tell stories in a graphic format.
- Photo Collages: Students take multiple photographs and combine them into a single collage using editing software, learning about composition and digital image manipulation.
- Creating a Short Film: Students work in groups to produce a short film or skit, writing scripts, acting, filming, and editing the final project.
- Analyzing Media Messages: Students analyze advertisements, TV shows, or news clips, discussing how the media messages are crafted and what techniques are used to convey specific messages or emotions.
Media arts education not only develops technical and creative skills but also encourages students to become critical consumers and producers of media. Through media arts, students learn how to communicate visually and verbally, gaining confidence in their ability to express ideas, tell stories, and present information in compelling ways. The ability to create, edit, and analyze media is a valuable skill that has wide applications, from school projects to future careers in creative industries. Media arts also encourage collaboration, as students often work together in groups to create and refine their media projects.
Legal Standards of Art in California Schools
California Arts Standards and Proposition 28
The California Arts Standards provide a framework for arts education in dance, media arts, music, theatre, and visual arts for students from pre-kindergarten through 12th grade. These standards, adopted in 2019, are based on the National Core Arts Standards and emphasize creativity, artistic expression, and critical thinking. The standards are structured around four artistic processes:
- Creating – Generating and developing artistic ideas and work.
- Performing/Producing/Presenting – Realizing and sharing artistic work through performance or presentation.
- Responding – Understanding and evaluating artistic works.
- Connecting – Relating artistic ideas and works to personal experiences, society, and history.
The standards ensure that all students, regardless of background, have access to a high-quality arts education that fosters self-expression, cultural awareness, and interdisciplinary learning. They emphasize that arts education is not just about performance or production but also about critical thinking, communication, and collaboration.
Proposition 28: The Arts and Music in Schools (2022)
In November 2022, California voters approved Proposition 28, which significantly increases funding for arts and music education in public schools. This law requires the state to allocate an additional amount of funding each year for arts programs, without raising taxes. The funding is expected to provide nearly $1 billion annually for arts education in K-12 public schools, with a focus on hiring more arts teachers, expanding arts programs, and increasing student access to the arts.
Key aspects of Proposition 28 include:
- Guaranteed funding for arts and music education based on a percentage of California’s general fund revenue.
- Priority for schools with high percentages of low-income students, ensuring equity in access to arts education.
- Funds must be used for arts education, including hiring teachers, purchasing supplies, and developing new programs.
Together, the California Arts Standards and Proposition 28 demonstrate the state’s commitment to ensuring that all students have access to a well-rounded education that includes the arts, recognizing their role in fostering creativity, innovation, and emotional well-being.
Arts in After-School Programs
Arts education in after-school programs provides students with creative enrichment, social engagement, and skill development beyond the regular school day. Programs such as those offered by the Boys & Girls Club and After School Education and Safety (ACES) play a vital role in ensuring that students have access to quality arts experiences. These programs introduce students to visual arts, music, dance, theatre, and media arts in a fun, engaging environment, allowing them to explore their creativity in ways that may not be possible during regular school hours. Unlike traditional classroom instruction, after-school arts programs offer flexibility and hands-on learning, where students can experiment with different artistic styles, collaborate with peers, and gain confidence in their abilities.
Participation in after-school arts programs has been shown to enhance academic performance, social-emotional skills, and self-confidence. Organizations like the Boys & Girls Club provide structured arts programs that encourage self-expression and teamwork, helping students develop critical thinking and communication skills. ACES-funded programs ensure that students—especially those from underserved communities—have access to enriching arts activities that support their personal, social, and academic growth. These programs also connect students with mentors, local artists, and cultural experiences, broadening their artistic horizons. By fostering a love for the arts, after-school programs empower students to become more creative, resilient, and engaged learners, preparing them for future success in school and beyond.
Conclusion
Arts education plays a vital role in supporting the academic, social, and emotional development of children, particularly in California’s diverse school communities. Research shows that participation in the arts is linked to higher academic achievement, increased civic engagement, and improved social-emotional outcomes, especially for youth from underserved backgrounds (National Endowment for the Arts, 2012). In California, the Department of Education emphasizes equitable access to quality arts education as a core part of a well-rounded curriculum, recognizing its value in fostering creativity, critical thinking, and cultural awareness. Programs such as those offered by the Boys & Girls Clubs of America and supported by the U.S. Department of Education’s Arts in Education initiative illustrate how structured, high-quality arts programming can engage students during and after school. Innovative out-of-school-time (OST) approaches, highlighted by the Afterschool Alliance (2023), further show how community-based partnerships can provide inclusive, student-centered opportunities that nurture talent and support youth expression. As California continues to prioritize whole-child development, the integration of arts programming in schools and OST settings is not just enriching, it’s essential.
Resources
- After School Alliance. (2023 October 17). Promising practices and innovative responses for high-quality arts programming in OST. https://www.afterschoolalliance.org/afterschoolsnack/Promising-practices-and-innovative-responses-for-high-quality_10-17-2023.cfm
- Boys & Girls Clubs of America. (n.d.). – Arts Programs. https://www.bgca.org/programs/the-arts/
- California Department of Education, Arts Education. www.cde.ca.gov
- National Endowment for the Arts. (2012). The Arts and Achievement in At-Risk Youth: Findings from Four Longitudinal Studies. https://www.arts.gov/sites/default/files/Arts-At-Risk-Youth.pdf (NEA Report) – NEA Study PDF
- U.S. Department of Education. (2025). , – Arts in Education National Program. https://www.ed.gov
Media Attributions
- Children_with_music © Admin, CC BY 2.5 adapted by Jocelynnjocy is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Children’s_Aesop © Mzilikazi1939 adapted by Ross Stapleton-Gray, CC BY-SA 4.0 is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
- Children_dancing_to_Gangnam_Style © Airman 1st Class Justin Veazie, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons is licensed under a Public Domain license
- A_child_taking_a_picture_of_his_friend © Bhavesh0487 is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license

